How to operate a drone? This seemingly simple question opens a world of exciting possibilities, from breathtaking aerial photography to efficient surveying and inspection. Mastering drone operation requires a blend of technical understanding, safety awareness, and responsible piloting. This guide provides a comprehensive walkthrough, covering everything from pre-flight checks to post-flight maintenance, ensuring you can confidently and safely take to the skies.
We’ll explore the intricacies of drone controls, flight planning, camera operation, and legal considerations. Whether you’re a complete beginner or seeking to refine your skills, this guide will equip you with the knowledge and confidence to navigate the world of drone piloting with ease and responsibility.
Pre-Flight Checklist and Safety Procedures
Before embarking on any drone flight, a thorough pre-flight checklist is crucial for ensuring both the safety of the drone and those in its vicinity. Neglecting these checks can lead to accidents, damage, and legal issues. This section details a comprehensive checklist and safe launch procedures.
Pre-Flight Checklist
A comprehensive pre-flight checklist ensures your drone is in optimal condition for flight. This involves checking various components and systems to mitigate potential risks.
- Battery Level: Ensure the battery is sufficiently charged and in good condition. A low battery can lead to unexpected power loss mid-flight.
- GPS Signal: Verify a strong GPS signal for accurate positioning and stability. A weak signal can result in inaccurate flight and potential crashes.
- Propeller Inspection: Carefully inspect each propeller for any damage, cracks, or imbalance. Damaged propellers can cause instability and failure.
- Gimbal Calibration (if applicable): If your drone has a gimbal, ensure it’s properly calibrated for smooth and stable camera operation.
- Radio Link Check: Test the connection between your drone and the remote controller to ensure a strong and reliable signal.
- Environmental Check: Assess wind conditions, visibility, and potential obstacles in the flight area.
Critical Pre-Flight Safety Procedures
| Procedure | Importance | Check Method | Potential Consequences of Failure |
|---|---|---|---|
| Battery Check | Ensures sufficient power for the flight. | Visual inspection of battery level indicator. | Unexpected power loss, leading to a crash. |
| GPS Signal Verification | Essential for accurate positioning and stability. | Check GPS signal strength on the controller screen. | Inaccurate flight, potential loss of control. |
| Propeller Inspection | Identifies potential damage that could cause instability. | Visual inspection for cracks, damage, or imbalance. | Propeller failure, leading to a crash. |
| Environmental Assessment | Ensures safe flight conditions. | Visual observation of weather and obstacles. | Flight in unsafe conditions, resulting in accidents or damage. |
Safe Drone Launch Procedure
- Find a clear, open area away from obstacles and people.
- Power on the remote controller first, then the drone.
- Wait for the GPS signal to lock.
- Carefully lift the drone off the ground, using gentle throttle inputs.
- Maintain visual contact with the drone at all times.
Understanding Drone Controls and Navigation
Understanding your drone’s controls is fundamental to safe and effective operation. This section explains basic controls, flight modes, and control interfaces.
Basic Drone Controls
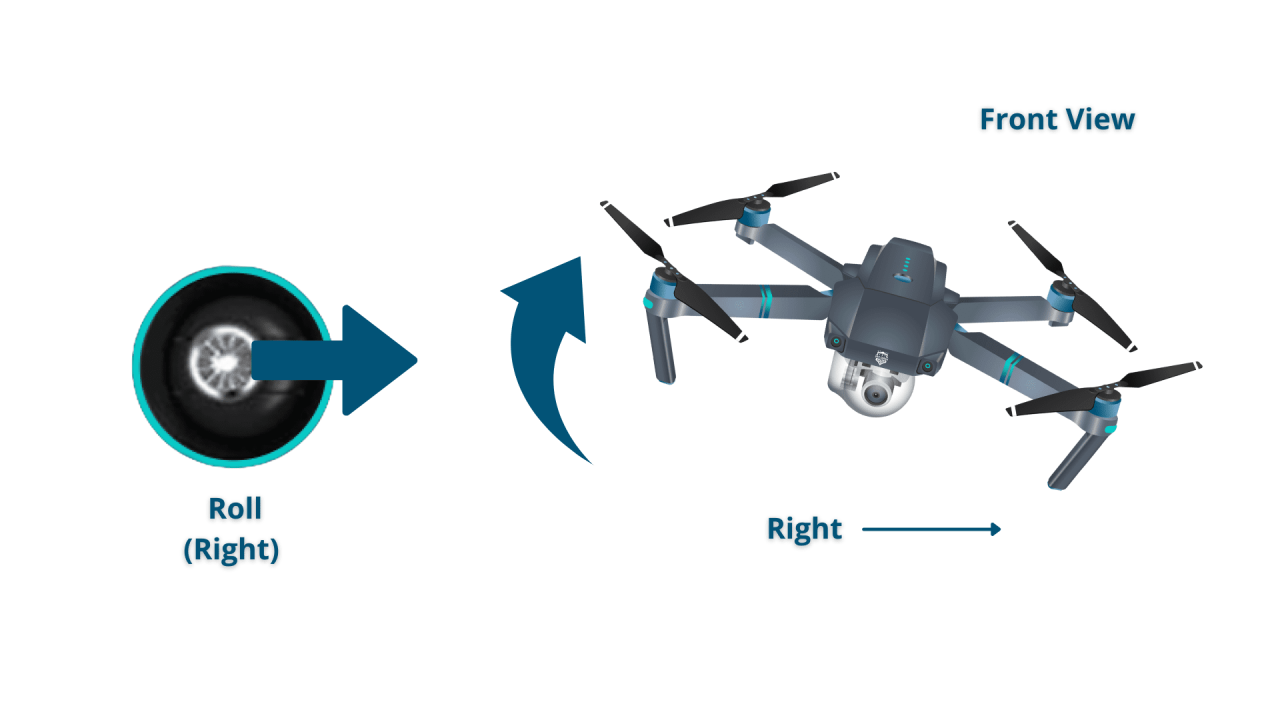
Most drones utilize two control sticks: one for controlling altitude and yaw (rotation), and the other for controlling pitch (forward/backward) and roll (left/right). Buttons on the controller are used for additional functions like camera control, return-to-home, and emergency stops. A visual representation of the stick movements could be described as follows: pushing the left stick forward moves the drone forward; pushing it right makes it move right.
Similarly, pushing the right stick forward increases the drone’s altitude and rotating it controls the yaw.
Flight Modes

Different flight modes offer varying levels of control and stability. Attitude mode provides direct control over the drone’s orientation, while GPS mode uses satellite data for positioning and stability. Return-to-home (RTH) mode automatically guides the drone back to its starting point.
Drone Control Interfaces
Many drones offer different control interfaces, including smartphone apps and dedicated remote controllers. Smartphone apps often provide more features and visual feedback, while dedicated controllers offer greater precision and responsiveness. The choice of interface depends on personal preference and the specific drone model.
Control Stick Movements and Drone Orientation
Imagine a three-dimensional coordinate system centered on the drone. The left stick controls movement along the X and Y axes (forward/backward and left/right), while the right stick controls movement along the Z axis (altitude) and rotation around the Z axis (yaw). Tilting the sticks diagonally combines these movements, allowing for precise maneuvering.
Flight Planning and Execution
Careful flight planning is essential for safe and successful drone operations. This involves identifying suitable flight zones, considering weather conditions, and understanding potential hazards.
Flight Planning Process
Before each flight, identify a safe flight zone free from obstacles and people. Check the weather forecast to ensure suitable conditions (low wind, good visibility). Plan your flight path, considering the drone’s battery life and range.
Maintaining Safe Distances
Always maintain a safe distance from obstacles and people during drone operation. Avoid flying near power lines, tall buildings, or crowds. Respect privacy and avoid flying over private property without permission.
Potential Hazards and Mitigation Strategies, How to operate a drone
- Obstacle Collisions: Use obstacle avoidance features if available, and maintain visual contact with the drone.
- Loss of Signal: Ensure a strong signal throughout the flight, and have a return-to-home function enabled.
- Adverse Weather: Avoid flying in strong winds, rain, or fog.
- Battery Failure: Always have sufficient battery power, and monitor the battery level during flight.
Using GPS Coordinates for Flight Path Planning
Many drone apps allow you to input GPS coordinates to plan a precise flight path. This is particularly useful for mapping, surveying, or photography projects. The app will guide the drone along the defined route, allowing for consistent and repeatable flights.
Drone Camera Operation and Image Capture
Understanding your drone’s camera settings is crucial for capturing high-quality photos and videos. This section explains camera settings, modes, and their applications.
Camera Settings and Image Quality
Aperture, shutter speed, and ISO are key camera settings that affect image quality. Aperture controls the depth of field (how much of the image is in focus), shutter speed controls motion blur, and ISO controls image sensitivity to light (affecting noise levels).
Capturing High-Quality Photos and Videos
To capture high-quality images, use appropriate settings for the lighting conditions. For sharp images, use a faster shutter speed, especially when shooting moving subjects. For low-light conditions, increase the ISO but be mindful of increased noise.
Drone Camera Modes
Different camera modes cater to various photography and videography needs. Photo mode captures still images, video mode records moving footage, and timelapse mode captures a sequence of images at set intervals to create a time-lapse video.
Comparison of Drone Camera Features

| Feature | Description | Suitability | Example Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| High Resolution Sensor | Provides detailed images with sharp clarity. | Ideal for professional photography and videography. | Real estate photography, landscape videography. |
| Wide Angle Lens | Captures a broad field of view. | Suitable for landscape photography and wide shots. | Aerial photography of large areas. |
| 4K Video Recording | Records high-resolution video footage. | Ideal for cinematic videos and detailed recordings. | Filmmaking, wildlife documentaries. |
| Gimbal Stabilization | Reduces camera shake for smoother footage. | Essential for stable videos and professional shots. | Aerial cinematography, drone racing. |
Post-Flight Procedures and Maintenance
Proper post-flight procedures and regular maintenance ensure the longevity and optimal performance of your drone. This section details safe landing, storage, and troubleshooting.
Safe Landing and Storage
- Slowly lower the drone to the ground using gentle throttle inputs.
- Power off the drone, then the remote controller.
- Store the drone in a clean, dry place, away from direct sunlight.
- Properly store and charge the batteries.
Drone Maintenance
Regular maintenance is crucial for the safe and reliable operation of your drone. This includes cleaning the drone body and propellers, checking for loose parts, and properly storing and maintaining the batteries.
Troubleshooting Common Drone Issues
Common issues include loss of signal, battery problems, and propeller damage. Refer to your drone’s manual for specific troubleshooting steps. For complex issues, contact the manufacturer or a qualified technician.
Recommended Maintenance Tasks
- Clean the drone body and propellers after each flight.
- Inspect the drone for loose parts or damage monthly.
- Check and calibrate the gimbal (if applicable) quarterly.
- Store batteries properly and charge them according to manufacturer recommendations.
Legal and Regulatory Compliance: How To Operate A Drone
Operating a drone responsibly involves adhering to local laws and regulations. This section highlights the importance of legal compliance.
Drone Regulations
Drone regulations vary by region and country. It is crucial to research and understand the specific rules and restrictions that apply in your area. These regulations often cover registration, flight restrictions (no-fly zones), and operational limitations.
Obtaining Permits and Licenses
In many areas, you may need to obtain permits or licenses before operating a drone, particularly for commercial use or flights in restricted airspace. Failure to obtain necessary permits can result in significant fines or legal penalties.
Successfully piloting a drone involves understanding its controls and adhering to safety regulations. Learning the basics is crucial before taking flight, and a great resource for this is the comprehensive guide on how to operate a drone , which covers pre-flight checks and essential maneuvers. Mastering these skills ensures safe and enjoyable drone operation.
Implications of Violating Drone Regulations
Violating drone regulations can lead to various consequences, including fines, drone confiscation, and even criminal charges. Responsible operation involves careful adherence to all applicable rules and regulations.
Best Practices for Responsible Drone Operation
- Register your drone according to your region’s regulations.
- Always check for no-fly zones before flying.
- Maintain visual line of sight with your drone.
- Respect privacy and avoid flying over private property without permission.
- Fly responsibly and safely, considering the well-being of others.
Successfully operating a drone involves more than just understanding the controls; it’s about embracing a responsible and safety-conscious approach. From meticulous pre-flight preparations to diligent post-flight maintenance, each step contributes to a safe and rewarding flying experience. By following the guidelines Artikeld in this guide, you can unlock the full potential of your drone while adhering to all necessary regulations and ensuring both your safety and the safety of those around you.
Safe flying!
Understanding drone operation involves mastering several key skills, from pre-flight checks to navigating airspace regulations. Learning how to safely and effectively control your drone is paramount, and a great resource for this is the comprehensive guide on how to operate a drone which covers everything from basic controls to advanced maneuvers. Ultimately, proficient drone operation requires consistent practice and a thorough understanding of safety procedures.
Commonly Asked Questions
What type of drone is best for beginners?
Many user-friendly drones are ideal for beginners, often featuring GPS assisted flight modes and automatic return-to-home functions. Look for drones with intuitive controls and good online support.
How often should I calibrate my drone’s compass?
Compass calibration is crucial for accurate flight. It’s recommended to calibrate before each flight, especially if you’ve moved to a new location or experienced any significant magnetic interference.
What should I do if my drone loses signal?
Most drones have a return-to-home (RTH) function. If signal is lost, the drone will attempt to return to its takeoff point. However, always ensure you have a clear line of sight to maintain control as much as possible.
How do I handle strong winds during flight?
Avoid flying in strong winds. If caught in unexpected wind gusts, gently lower your drone and land it as soon as it’s safe to do so.